The Trendelenburg position is a method of patient positioning used in healthcare facilities. In this article, we will learn what the Trendelenburg position is and what its main uses are. We will also look at the differences between the Trendelenburg position and the reverse Trendelenburg position.
What is the Trendelenburg position?
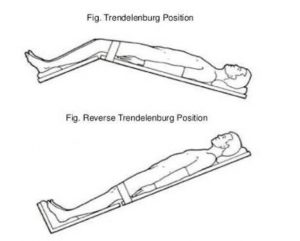
The Trendelenburg position, also known as the dorsosacral or the dorsal decline position, is a patient positioning used to relieve certain discomforts and perform surgical procedures. When the patients are placed in the Trendelenburg position, they lie flat on their back with their feet set higher than the head at a degree of inclination, typically between 5 and 30 degrees.
This position is usually adopted from a hospital bed, stretcher, or medical examination table since it requires the patient to lie on their back on a flat surface. However, some treatment chairs with a backrest and leg rest that can be tilted completely flat also allow the patient to be placed in this position.
The Trendelenburg position cannot be assumed from the floor, as the patient must be on a flat surface that can be tilted. Thus, if a patient falls to the floor in discomfort, medical personnel must move the patient to a stretcher or appropriate treatment chair before the patient can be placed in the Trendelenburg position.
When to use the Trendelenburg position?
The Trendelenburg position is primarily used for abdominal and gynecological surgery. When a patient is placed in this position, his organs move upward under gravity. This improves access to specific organs during surgery in the pelvic region. Healthcare professionals also use the Trendelenburg position to place or remove a central venous catheter in a patient’s internal jugular or subclavian vein.
The Trendelenburg position is also used in the event of hypotensive or vagal discomfort in the patient. Indeed, placing the patient in the Trendelenburg position is often the first emergency measure used in the event of a sudden drop in blood pressure or a brief loss of consciousness. This positioning aims to increase blood flow to the heart and brain.
Specialists point out that caution should be exercised when using the Trendelenburg position, as certain risks are associated with this patient positioning. For example, the Trendelenburg position is contraindicated in obese patients because it can cause breathing difficulties. In addition, because it increases intracranial and intraocular pressure, the Trendelenburg position is contraindicated in patients with intracranial hypertension or head injury.
What is the difference between the Trendelenburg position and the reverse Trendelenburg position?
Physically, the main difference between the two positions is the orientation of the patient’s inclination. Classic Trendelenburg is a decline position: the patient’s head is placed lower than his feet. Conversely, reverse Trendelenburg is a pro-Trendelenburg position: the patient’s head is higher than his feet. Thus, in the Trendelenburg position, the foot of the bed is raised to create the tilt; in the reverse Trendelenburg position, it is instead the head of the bed that is raised.
The two positions also differ in their use. The reverse Trendelenburg position is used, among other things, to relieve gastroesophageal reflux and intracranial pressure. In surgery, it is used to reduce blood loss during neck and head procedures. If you want to learn more about the reverse Trendelenburg position and its main uses, we invite you to read our article, reverse Trendelenburg.
In summary
Recall that the Trendelenburg position consists of laying the patient flat, on his back, with his head lower than the lower limbs. This position is mainly used during abdominal and pelvic surgery. It is also used to relieve hypotension or to treat vagal discomfort. Medical personnel must have stretchers and treatment chairs designed to perform this maneuver ergonomically and safely to prevent the risk of injury when positioning the patient.
If you would like to learn more about ergonomic medical equipment that can place the patient in the Trendelenburg position, please feel free to speak with one of our experts.
Contact us
